Spinal Cord Injuries: Causes, Symptoms, and Recovery
Spinal cord injuries, often caused by traumatic events like car accidents or falls, can have devastating effects on individuals. The symptoms, ranging from partial or complete paralysis to loss of sensation, highlight the urgent need for more awareness and support for those affected.
Introduction
Spinal cord injuries (SCIs) can have a life-altering impact on individuals, affecting their mobility, independence, and overall quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial for both prevention and recovery. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about spinal cord injuries and how individuals can regain function and lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges.
What Is a Spinal Cord Injury?
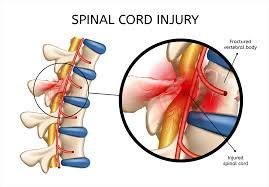
A spinal cord injury occurs when the spinal cord is damaged due to trauma, disease, or degenerative conditions. The spinal cord is a vital structure that transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body, making it essential for movement, sensation, and bodily functions. Damage to the Spinal Cord Injury can lead to temporary or permanent loss of function below the site of injury.
Common Causes of Spinal Cord Injuries
Spinal cord injuries can result from various incidents, including:
1. Traumatic Injuries
-
Motor Vehicle Accidents: Leading cause of SCIs worldwide, often due to high-impact crashes.
-
Falls: Especially common in older adults and workplace accidents.
-
Sports Injuries: High-contact sports like football, gymnastics, and diving carry a higher risk.
-
Violence: Gunshot wounds and stabbings can damage the spinal cord directly.
2. Non-Traumatic Injuries
-
Degenerative Diseases: Conditions like arthritis and osteoporosis can weaken the spine.
-
Infections: Meningitis and spinal tuberculosis can lead to inflammation and damage.
-
Tumors: Abnormal growths can press on the spinal cord, causing dysfunction.
-
Autoimmune Disorders: Multiple sclerosis and other immune conditions can deteriorate nerve function.
Types of Spinal Cord Injuries
Spinal cord injuries are classified based on the severity and location of the damage.
1. Complete vs. Incomplete Injuries
-
Complete SCI: Total loss of motor and sensory function below the injury site.
-
Incomplete SCI: Partial loss of function, with some signals still transmitted.
2. Level of Injury
-
Cervical (Neck) Injuries: Can lead to quadriplegia (paralysis of all limbs).
-
Thoracic (Upper Back) Injuries: May affect chest and legs, potentially causing paraplegia.
-
Lumbar (Lower Back) Injuries: Primarily affects legs and lower body functions.
-
Sacral (Pelvic Region) Injuries: Often impact bladder, bowel, and sexual functions.
Symptoms of Spinal Cord Injuries
The symptoms of a spinal cord injury vary depending on the location and severity of the damage.
Common Signs Include:
-
Loss of movement and coordination
-
Numbness or tingling in limbs
-
Difficulty breathing (in high spinal injuries)
-
Loss of bowel and bladder control
-
Intense pain or pressure in the neck, back, or head
Diagnosing a Spinal Cord Injury
Medical professionals use several methods to diagnose SCIs, such as:
-
Physical Examination: Assessing motor function and reflexes.
-
Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to detect fractures or damage.
-
Neurological Tests: Evaluating nerve function and sensation.
Treatment Options for Spinal Cord Injuries
Treatment for SCIs focuses on stabilizing the patient, preventing further damage, and promoting recovery.
1. Emergency Care
-
Immobilization to prevent worsening of the injury.
-
Oxygen therapy for breathing support.
-
Surgery to remove bone fragments or relieve pressure.
2. Rehabilitation
-
Physical Therapy: Exercises to maintain muscle strength and flexibility.
-
Occupational Therapy: Training for daily tasks and assistive device usage.
-
Psychological Support: Addressing mental health challenges post-injury.
3. Medications
-
Steroids: Reduce inflammation and swelling.
-
Pain Relievers: Manage chronic pain and discomfort.
-
Muscle Relaxants: Help with muscle spasms and stiffness.
4. Assistive Technologies
-
Wheelchairs and Mobility Aids: Improve independence and mobility.
-
Neuroprosthetics: Devices that stimulate nerve function.
-
Exoskeletons: Wearable robotic suits aiding in movement.
Advances in Spinal Cord Injury Research
Recent scientific breakthroughs offer hope for improved treatment outcomes.
1. Stem Cell Therapy
-
Promotes nerve regeneration and repair.
2. Epidural Stimulation
-
Electrical stimulation to activate paralyzed muscles.
3. Gene Therapy
-
Targeting specific genes to enhance nerve healing.
Coping with Life After a Spinal Cord Injury
Living with an SCI requires lifestyle adjustments and strong support systems.
1. Mental and Emotional Well-being
-
Therapy and counseling for depression and anxiety.
-
Support groups for sharing experiences and motivation.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
-
Home adaptations for accessibility.
-
Nutrition and exercise for overall health.
3. Employment and Independence
-
Workplace accommodations for SCI individuals.
-
Skill development and adaptive technologies for career opportunities.
Preventing Spinal Cord Injuries
While not all SCIs are preventable, taking precautions can significantly reduce risk.
Tips for Prevention:
-
Always wear seat belts and helmets.
-
Avoid high-risk activities without proper training.
-
Maintain bone health through diet and exercise.
-
Regular medical check-ups for early disease detection.
Conclusion
Spinal cord injuries can present significant challenges, but with advancements in medicine, rehabilitation, and assistive technology, many individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Awareness, prevention, and research remain key to improving SCI outcomes. By staying informed and taking proactive steps, individuals and families can navigate the journey toward recovery and independence more effectively.
What's Your Reaction?












