Magnesium Selenate Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2025: Manufacturing Plant Setup and Operations
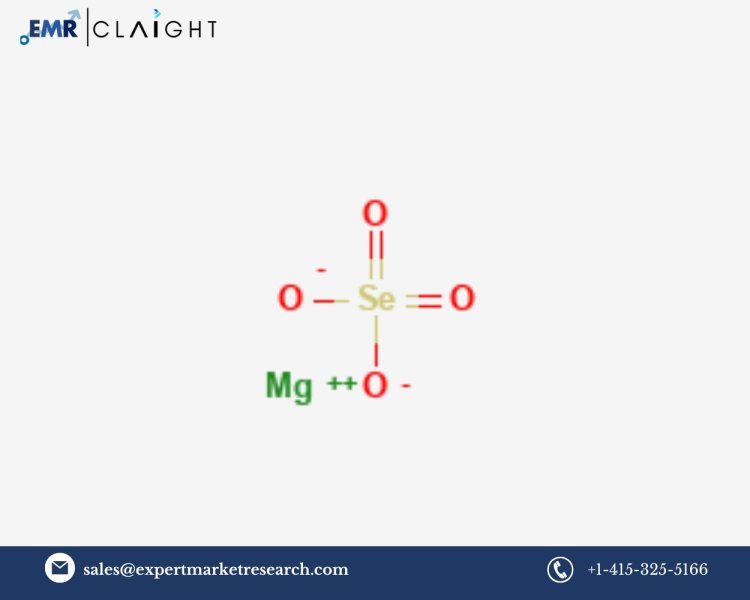
Introduction
The Magnesium Selenate Manufacturing Plant Project Report provides a detailed guide for setting up a facility to produce magnesium selenate, a chemical compound used in agriculture, industry, and health applications. Magnesium selenate, composed of magnesium and selenium, plays a vital role in soil nutrition and plant growth. It is increasingly used as a fertilizer additive in farming practices and in various industrial processes. With the growing awareness of the importance of selenium in human and animal health, the demand for magnesium selenate has risen, making it a lucrative opportunity for businesses looking to invest in the chemical manufacturing sector.
Market Overview and Demand
The demand for magnesium selenate has been increasing in several industries due to its beneficial properties, particularly in agriculture and health. The key drivers for the demand in these sectors include:
-
Agricultural Industry: Magnesium selenate is used as a trace element in fertilizers, as selenium is essential for the proper growth of crops and plants. It plays a significant role in improving soil fertility and promoting better yield in selenium-deficient regions.
-
Health and Nutrition: Magnesium selenate is increasingly used in supplements and food additives due to its selenium content. Selenium is vital for human health as it supports immune function and acts as an antioxidant. It also plays a crucial role in thyroid function and preventing cellular damage.
-
Animal Feed Industry: Magnesium selenate is used as a supplement in animal feed to ensure animals receive adequate selenium for better health, growth, and reproduction.
-
Industrial Applications: Magnesium selenate is utilized in the chemical industry as a raw material for the synthesis of other selenium compounds, which are used in electronics, photovoltaics, and other specialized applications.
-
Environmental Sustainability: As agriculture moves towards more sustainable practices, the role of trace minerals like selenium becomes more important, driving the demand for magnesium selenate in organic farming and eco-friendly fertilization techniques.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Objectives of the Magnesium Selenate Manufacturing Plant
The main objectives of establishing a magnesium selenate manufacturing plant include:
- Production of High-Quality Magnesium Selenate: To produce magnesium selenate with high purity and consistency to meet industry standards.
- Cost-Efficient Manufacturing: To minimize production costs through optimized processes and efficient raw material usage.
- Meeting Market Demand: To cater to the growing demand for magnesium selenate in agriculture, nutrition, and industrial applications.
- Sustainable Practices: To incorporate eco-friendly technologies and minimize environmental impact during the manufacturing process.
- Innovative Product Development: To explore new formulations of magnesium selenate that can serve specialized needs in agriculture and health.
Manufacturing Process of Magnesium Selenate
The process of manufacturing magnesium selenate involves several key stages, starting from raw material procurement to the final product. Below is an outline of the steps involved:
1. Raw Material Sourcing
The primary raw materials required for the production of magnesium selenate include:
- Magnesium Carbonate: Magnesium carbonate is used as the magnesium source.
- Selenium Dioxide: Selenium dioxide is the source of selenium for magnesium selenate.
- Sulfuric Acid: Sulfuric acid is used to react with magnesium carbonate to form magnesium sulfate, an intermediate compound in the process.
- Water: Water is required for dissolving and mixing the chemical compounds during production.
2. Preparation of Magnesium Sulfate
Magnesium sulfate is first produced by reacting magnesium carbonate with sulfuric acid in a reaction vessel.
3. Selenium Addition
Selenium dioxide is then added to the magnesium sulfate solution. The selenium reacts with magnesium sulfate in the presence of water to form magnesium selenate.
4. Purification and Crystallization
The solution is then cooled, and magnesium selenate begins to crystallize. The crystals are filtered from the solution and washed thoroughly to remove any impurities, such as excess sulfuric acid or selenium dioxide.
5. Drying and Milling
The purified magnesium selenate is dried in a controlled environment to remove excess moisture. The dried product is then milled to the required particle size. The final product can range from fine powder to granular form, depending on the specifications required by end users.
6. Quality Control
Before packaging, the magnesium selenate undergoes rigorous quality control tests to ensure that it meets the required standards for purity, consistency, and particle size. These tests typically include:
- Purity Testing: To confirm that the product contains the correct amount of selenium and magnesium.
- Particle Size Analysis: To ensure that the product is suitable for its intended applications.
- Moisture Content: To ensure that the product is sufficiently dried and has no residual moisture.
- Chemical Composition: To verify the ratio of magnesium and selenium in the final product.
7. Packaging
Once the product has passed quality control, it is packaged in moisture-proof containers to maintain its quality during storage and transportation. Packaging can include bags, drums, or bulk containers, depending on customer needs.
Equipment and Technology Requirements
Setting up a magnesium selenate manufacturing plant requires specialized equipment and technology to ensure smooth production and quality control. The following equipment is essential:
- Reaction Vessels: For the initial reaction between magnesium carbonate and sulfuric acid.
- Selenium Dioxide Addition Systems: For introducing selenium dioxide into the solution.
- Crystallization Units: For promoting the formation of magnesium selenate crystals.
- Filtration Units: To separate the crystallized magnesium selenate from the solution.
- Drying Equipment: To remove moisture from the final product.
- Milling Machines: For grinding the dried magnesium selenate into the desired powder or granular form.
- Quality Control Labs: To test the purity, particle size, and chemical composition of the magnesium selenate.
- Packaging Machines: For packaging the product in suitable containers.
Investment and Financial Projections
The investment required to establish a magnesium selenate manufacturing plant depends on several factors, including plant size, location, and equipment. The key investment components include:
-
Capital Investment:
- Plant Construction: Building the facility and installing infrastructure.
- Machinery and Equipment: Purchasing reaction vessels, crystallization units, dryers, and milling machines.
- Raw Materials: Sourcing magnesium carbonate, selenium dioxide, sulfuric acid, and other chemicals.
- Labor: Hiring skilled personnel for operations and quality control.
-
Operating Costs:
- Raw Material Procurement: Continuous purchase of magnesium carbonate, selenium dioxide, and sulfuric acid.
- Energy Consumption: Energy for the heating, drying, and milling processes.
- Labor Costs: Salaries for plant staff and management.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance of machinery and equipment.
-
Revenue Generation:
- The revenue will primarily come from the sale of magnesium selenate to agricultural, nutritional, and industrial customers. Pricing will depend on purity, packaging, and market demand.
-
Return on Investment (ROI):
- A well-established plant can begin generating profits within 2-3 years, depending on market conditions, production efficiency, and operational costs.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
To ensure safe and high-quality production, the magnesium selenate manufacturing plant must comply with various regulatory standards:
- Environmental Regulations: The plant must adhere to environmental guidelines regarding emissions, waste disposal, and water usage.
- Health and Safety Standards: Compliance with health and safety regulations to protect workers handling chemicals and hazardous materials.
- ISO Certifications: Obtaining ISO certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management to improve operational standards and gain market credibility.
- Chemical Handling Standards: Compliance with regulations related to the safe handling and storage of selenium and other chemicals.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au
What's Your Reaction?













